Using the Geobroker to Manage Your Resources
The Geobroker has information on the validation status of your resources both on your local GDRS and the central GDRS. It is also the place where you manage the distribution of your resources. Below is a guide to interpreting its contents.
Login
- Go to http://geobroker.gisdata.mn.gov/
- Click Login
- Enter Username and Password (You receive a user name and password when you register as a publisher)
- Click Login Button
Getting to know the GeoBroker Dashboard
- After Logging in, click on Manage distribution of Resources.
- You will now see your Geobroker Dashboard. When you registered as a publisher you were granted publishing rights for one or more publishers. On the dashboard you will see the publishers for which you have the authority to approve resource distributions. For each data resource or app resource in the Geobroker, you will get a report on the validity of the resource.
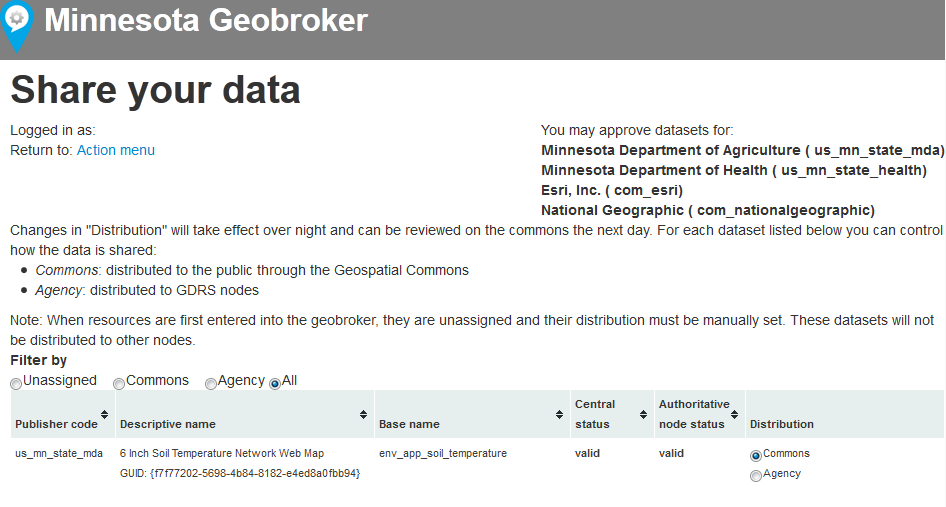
- Below is a key to interpreting the field headings:
- Publisher Code: Assigned to publishers at sign up. Publisher Code is used in organizing the GDRS and is found in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml.
- Descriptive Name: Descriptive Name is extracted from the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml. (Changes to this name are allowed, but will only appear here with administrative intervention. As a publisher, you are the only one who sees this name.) The second line is the Parent or Main Resource GUID (subResources also have a GUID, but they are not shown in the Geobroker dashboard record).
- Base Name: Base Name is the name of the root directory (folder) of the resource, and must match what is found in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml. It must also be unique in the GDRS. Rules for creating the Base Name are outlined in Data Resource Directory Structure and App Resource Directory Structure.
- Central Status: The validity of the resource on the Central GDRS. Valid means it has no errors or warnings. See below for more detail on interpreting the reports in the event of a warning and or error.
- Authoritative node status: This is the status on your node, if you have a local GDRS, or the status of the latest version you posted to the inbound FTP site if you use that for publishing. In the event that you are publishing new resources or updating an existing resource, this will provide you feedback, before your resource even reaches the central node, or explain why it is not reaching the central node. The error messages are very useful and thorough, but missing or blank can also refer to missing metadata.xml elements, not just dataResource.xml or appResource.xml elements.
- Distribution: Who is the resource being shared with? There are three settings:
- Commons: Distributed to the public through the Geospatial Commons.
- Agency: Distributed to other GDRS nodes only.
- Unassigned: Not shared beyond the Authoritative Node. These are local resources which your organization does not intend to share with any other organizations. These resources are essentially not published. This is the default, until you indicate that the resource should be distributed to "Agency" or "Commons" using the radio buttons.
Managing the Distribution of Resources
As discussed in the previous section, there are three distribution states and understanding how they work is important to making sure your resources are distributed to the intended target audience(s).
Distribution Ranges
None: Resource is not distributed.
Agency (or GDRS): Resource is shared to networked GDRS nodes, but not to the Commons FTP.
Commons: Resource is shared to networked GDRS nodes and to Commons FTP, for sharing with the full public.
Validation via the Geobroker
If you have used the Data Resource Editor to create your resource, or the Validation Tool to validate it, some of the validations steps have been completed before your resource reaches the Geobroker, and the publishing process should go more smoothly. The Geobroker validation performs some of the same checks as the other tools:
- Structure and content of metadata.xml file
- Structure and content of data resource or app resource folder, and whether that structure and content matches what is described in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml
- Validity of dataResource.xml and appResource.xml (required fields are filled in)
- Validity of data resource or app resource name (and whether it matches internally).
- Existence of only valid data distribution formats within the data resource.
In addition, the Geobroker performs some system-wide checks, including looking for duplicate GUIDs or duplicate resource names. It also automatically assigns resourceGUIDs and subResourceGUIDs if any of those elements are blank.
Interpreting Status Reports and Troubleshooting Tips
There are a range of status notifications which relate to the rigor of the documentation and the organization of the directory structure. Below is an overview of the statuses and following that a more detailed description of resolving errors and warnings.
Status Types
Valid: No issues, can be distributed as widely as desired.
Warning: Not fully conforming to standards, but the issues with the resource do no preclude it from full distribution on the Commons. A common issue would be a missing preview file, missing optional elements in the metadata.xml file. Fixing these issues would make a more robust package for users, but the fixes are not required.
mgc_error: Resource conforms enough to be shared between GDRS nodes, but has issues that must be addressed before it can be shared on the MN Geospatial Commons. This is most likely an issue with the metadata (dataResource.xml. appResource.xml, and or metadata.xml) files. Mandatory elements in these files may be missing or incorrect.
gdrs_error: Resource is missing basic elements, like metadata.xml. Therefore it will not be published anywhere.
Reports and Troubleshooting
Unless a resource is marked valid, there will be an accompanying report. Below are common error messages and how to resolve them:
GDRS ERRORS:
- gdrsEcosystemGUID: invalid or missing GUID
- Correction: Use GUID generator to get unique GUID.
- XXXXXXX: missing or blank
- This refers to elements in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, which are required for your resources to be shared via GDRS.
- Correction: Using MGC Resource Editor or text editor, edit your dataResource.xml or appResource.xml to include the missing elements.
- metadata.xml: NOT FOUND
- Correction: Place MGMG compliant metadata.xml and metadata.html in metadata subdirectory. Rename as "metadata.xml" and "metadata.html" if necessary. The Geobroker does not recognize the metadata files by any other names.
- topicCategory type="ISO 19115"
- missing
- Correction: Add one or more topic categories to your dataResource.xml.
- invalid value(s) XXXXXXX not in domain
- Correction: Refer to list of acceptable topic categories and correct dataResource.xml, as needed.
- missing
MGC ERRORS:
- ../dataResource_Parent_Directory/dataResource.xml - {'subResources': 'no subresources found in resource XML file'}
- Correction: Every subResource directory needs an a properly formatted element in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml.
- See additional help for setting up a dataResource or an appResource.
- metadata.xml:
- XXXXXXX: empty required element
- Correction: Edit metadata either with Minnesota Metadata Editor (LINK) or by hand. After editing metadata.xml, be sure to convert to metadata.html. Include both files in dataResource metadata subdirectory, both are required.
- XXXXXXX: empty required element
- publisherID: invalid value XXXXXXX not in domain
- Correction: Refer to correspondence when you signed up to be a publisher. It will be of the format us_mn_state_mngeo, which in most cases translates to reverse URL with slashes in the place of periods.
- See also this list of current publishers.
- XXXXXXX: missing or blank
- This refers to elements in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, which are required for your resources to be shared on the Commons.
- Correction: Using MGC Resource Editor or text editor, edit your dataResource.xml or appResource.xml to include the missing elements.
- XXXXXXX subResource tag missing or blank
- This refers to elements in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, which are required for your resources to be shared on the Commons.
- Correction: Using MGC Resource Editor or text editor, edit your dataResource.xml or appResource.xml to include the missing elements.
- subResourceGUID (These errors should be rare as the GeoBroker should automatically assign a GUID when the element is blank.)
- subResourceGUID missing
- Correction: Use GUID generator to get unique GUID and insert in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml.
- invalid value
- Correction: Use GUID generator to get unique GUID and insert in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml.
- subResourceGUID missing
- subResourceType: invalid value XXXXXXX not in domain
- Correction: Refer to resource type domains and correct dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, as needed. Note: Not all of the valid subResource Type domains on this list have been implemented in the Commons. If your subResource Type is on this list and you still get this error, contact gisinfo.mngeo@state.mn.us.
- subResourceAccess URL Type: invalid value(s) XXXXXXX not in domain
- Correction: Refer to URL type domains and correct dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, as needed.
WARNINGS:
- XXXXXXX: missing or blank
- This refers to elements in the dataResource.xml or appResource.xml, which are optional for your resources to be shared on the Commons.
- Correction: Using MGC Resource Editor or text editor, edit your dataResource.xml or appResource.xml to include the missing elements.
- missing or blank contact tag XXXXXXX
- Specific to appResources this pertains to contact information in the appResource.xml, which is used in lieu of MGMG metadata, for non-data type resource, such as apps, maps, and some services.
- Correction: Using MGC Resource Editor or text editor, edit your dataResource.xml or appResource.xml to include the missing elements.
Central Status Notes
Once your resource has been validated on the Central node during overnight publishing, if there are still errors or warnings, you will have an additional report available in the "Central status" column. Generally this report will show the same information as the "Authoritative node status" column, with one addition: a "Central node revision date" section that tells you the modified date and time of the data currently residing in the Central node. If this date is older than the data in your authoritative node, you know that a central validation check will occur again the next weeknight.
Repairing More Serious Errors
If your new data resource does not appear in the Geobroker list at all, consult the GDRS System Error Logs: gdrs:\system\logs and look at the most recent log file for indications of the error. Log files are generated hourly as the Geobroker validation is run on your node. Errors that prevent a resource from appearing in the Geobroker include:
- Duplicate resource GUID
- Duplicate resource name
Timing of Corrections
Geobroker validation timing is determined by each agency. Most agencies run validation checks hourly, but at different times. Knowing your agency's validation schedule, you can view the Geobroker validation results, make the necessary changes to your metadata.xml, system xml's (dataResource.xml or appResource.xml) and resource folder structure, and view the Geobroker results again after the next validation. When your resource has validated, make sure it is marked for "Agency" or "Commons" distribution, as appropriate. Publishing to other GDRS node and the Commons occurs overnight.
Viewing Published Records
If publisher distribution status is "Agency", this resource will appear in the Central GDRS and in other organizations' GDRS nodes as a new resource name under your publisher name. (You will not see a difference on your own GDRS node, because as the Authoritative node for that resource, you have already copied it there).
If publisher distribution status is "Commons", a searchable record will appear on the Minnesota Geospatial Commons under your publisher code. The zipped data or app will appear on the Commons ftp distribution site.
Once published, you can check the way a record looks on the Commons. You have a successful record, but it might be possible to improve it:
- On the resource list (before you click on your resource's link and go to that resource's main page) - is the title clear? Can you understand what the resource is? While the text of a title can be long, it is desirable to include main theme, area covered, and year (if appropriate) in the first 75 characters so that, even if truncated, it is obvious what the resource is. The basic characteristics of the resource should be understandable without opening up the resource record.
- Is the Abstract clear? Do any odd alphanumeric characters show up in the Abstract? Is there any additional information that should show up in the metadata Abstract, Publisher, or Time Period fields so that the most important information about the resource appears to the user first?
- Is the geographic extent correct? (Check the map).
These readability issues can be repaired (usually as edits to the metadata), recopied to the GDRS or Inbound FTP, and will appear corrected in the Commons the next day.
